DNA Transposons
A small mobile
genetic element (DNA) that moves around the genome or to other genomes within
the same cell, usually by copying itself to a second site but sometimes by
splicing itself out of its original site and inserting in a new location within
the same or another chromosome, plasmid, or cell and thereby transferring
genetic properties.
Transposons
have been used for transgenesis and insertional mutagenesis in different
organisms, since these elements are not generally dependent on host factors to
mediate their mobility. Consequently, DNA transposons are useful tools to
analyze the regulatory genome, study embryonic development, identify genes and
pathways implicated in disease or pathogenesis of pathogens, and even
contribute to gene therapy.
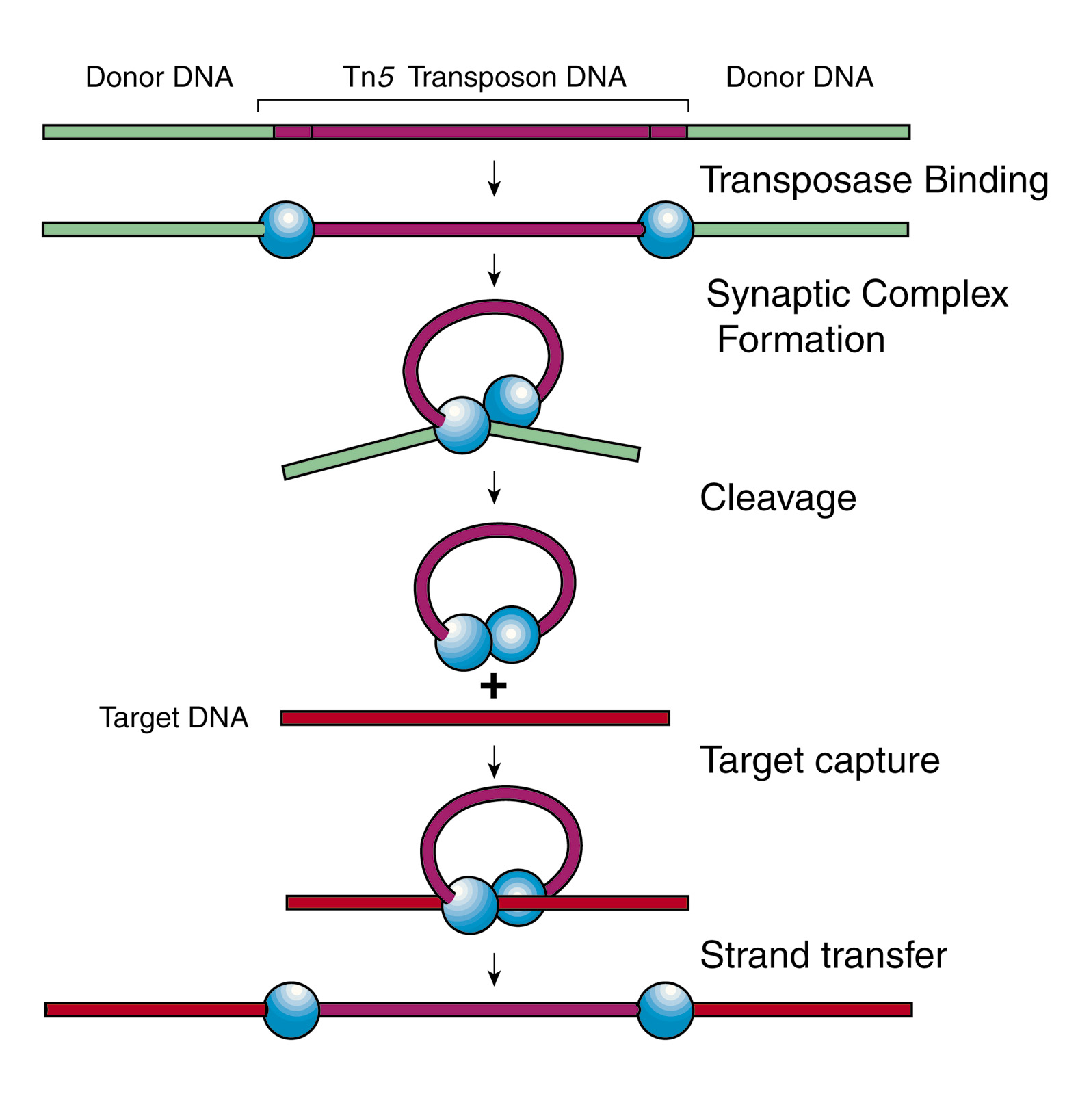 |
| Fig. 1: DNA transposon example |
No comments:
Post a Comment